Whenever most people think of a toothache, they see some form of transitory pain or suffering that can easily be treated with pain reducer meditation or household remedies. Nevertheless, an infection of a tooth is much more severe than a toothache. When it is not treated it may extend outside the mouth and be life threatening. The severity of dental abscess is something that many individuals do not give enough attention to, yet they must be aware of the risks and signs, as well as the stages of treatment that must be followed to safeguard not only health but also life, perhaps.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
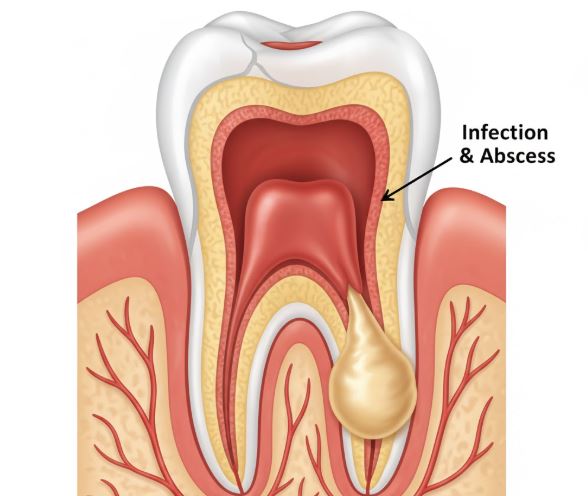
Tooth infection or dental abscess is the occurrence of bacteria to attack the innermost layer of the tooth, the pulp, which comprises nerves and blood vessels. The cause of this infection is usually untreated cavities, gum disease or some trauma which enables bacteria to enter the tooth. When the bacteria enter, they multiply causing a pus accumulation, swelling and extreme pain.
Dental abscesses are of three major types:
- Periapical abscess: This is located at the end of the tooth root most times because of the tooth decay left untreated.
- Periodontal abscess: This is evident in the gums and shows around the gum of the tooth, which is normally occasioned by gum disease.
- Gingival abscess: It is found in the gum and this is usually provoked by the availability of foreign bodies like food particles.
The Riskiness of a Tooth Infection.
A tooth abscess may start as a localized infection, but because of its rapid spreadability, it may readily lead to other body parts getting infected when untreated. The presence of blood vessels is easy in the mouth and the bacteria may also easily enter into the bloodstream leading to a deadly condition called sepsis. The infection may also be transmitted to the jawbone, neck, sinuses and even the brain all of which may have serious complications.
The severity of a tooth infection is also stipulated by several factors and these involve immune system, overall health and when one is infected.The especially vulnerable to complications are the diabetics, immunodeficient individuals and heart-problem patients.
How Soon Will a Tooth Infection Become Fatal?
Precisely, the duration of the infection will be dependent on the person and the prevalence of the infection, but in certain cases, an infection in the tooth may be fatal in a few days or weeks.
The infection is usually initiated in the pulp of the tooth and develops in the following way:
- Day 1-3: Mild to severe toothache, affected tooth swelling, hot or cold painfulness.
- Day 3-7: The infection can spread to the nearby tissues and result in the face swelling, fever, and the inability to open the mouth or swallow.
- During the 1-2 weeks: During this time, unless this is treated, bacteria might enter blood or vital organs of the body such as the jaw, neck, or brains.At this point, it can cause septic shock, brain abscess, or Ludwig angina (infectious fatal disease of the tongue and jaw) they are all fatal.
Reports have been made of people dying as a result of dental abscesses and this death had taken place within the span of a few days after the sickness had been contracted. So it is impossible to forget about the tooth infection.
When a Tooth Infection Is Spreading: Warning Signs.
- Seldom could swallow or breathe.
- Fever, chills, or fatigue
- Bad taste or strange smell on the tongue.
- The discharge of pus or fluid in place of infection.
- imbibed bleeding gums or exposed abscess.
The inflation of the neck or the beginning to block lung airflow is an emergency situation, and in this case, the neck should be intervened upon as soon as possible.
Treatment of Tooth infection.
Fortunately, tooth infections are treatable health care wise and focus on elimination of infection and pain reliever, and prevention of infection.The following may be prescribed by a dentist or a doctor:
- Root canal treatment: This is a procedure that removes infected pulp and bacteria of the tooth preserving the natural tooth structure.
- Tooth extraction: The tooth might have to be extracted in case it is too damaged.
- Antibiotics: These are taken in order to eliminate bacteria especially when the infection has spread to other body parts.
- Pain management: Pain during the recovery can be reduced by use of over-the-counter pain medication or prescription pain medication.
In severe situations when the infection is already penetrated, the person can be hospitalized and provide intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
Tooth Infections Prevention
It is always good to prevent rather than to cure. One can avoid infections through keeping your mouth clean and visiting your dentist regularly. Some prescription are the following:
- Limit sweets and drinks causing decadence.
- Have your toothbrush impregnated after every 34 months.
- Treatment of cavities, broken teeth or gum disease, time sensitive.
Early intervention can help to avoid a small dental problem that may develop into a severe infection.
Conclusion
Tooth infection is not something one can ignore and work on at home using some temporary meditation. What may start as a mere nuisance, may turn out to be a severe medical emergency should the condition be not addressed. Extremely, a dental abscess may be life threatening in the course of days to weeks. Timely dental care is good news as it will help to avoid complications and guarantee complete recovery.